This is my answer, but I've not found other descriptions of this simple model.
The Klein-Gordon wave equation of motion in the Robertson-Walker (RW) metric with scale factor \(a(t)\) as a function of time,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} { - 1,}&{\frac{{{a^2}(t)}}{{1 - K{r^2}}},}&{{a^2}(t){r^2},}&{{a^2}(t){r^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta } \end{array}\]is
\[\psi ''(t) = - 3H(t)\psi '(t) - {\omega ^2}\psi (t)\]
where \(H(t)\)is the Hubble parameter defined in terms of the scale factor.
\[H\left( t \right) = \frac{{\dot a\left( t \right)}}{{a\left( t \right)}}\]
and the constant frequency with units \({\text{secon}}{{\text{d}}^{ - 1}}\),
\(\omega = \frac{{{{\text{M}}_{KG}}{{\text{c}}^2}}}{\hbar }\)
The canonical energy-momentum tensor for the KG wave equation is diagonal with two independent components (0,0), (1,1) which are the matter and pressure energy density.
\(\mu = \hbar {\omega ^{ - 1}}{\psi '^*}\psi ' + {{\text{M}}_{KG}}{{\text{c}}^2}{\psi ^*}\psi \)
\(p = \hbar {\omega ^{ - 1}}{\psi '^*}\psi ' - {{\text{M}}_{KG}}{{\text{c}}^2}{\psi ^*}\psi \)
The time derivative of the real-valued densities is provided by the KG wave equation.
\(\dot \mu = - 3H(p + \mu )\)
\({\left( {\dot p - \dot \mu } \right)^2} = 4{\omega ^2}\left( {{\mu ^2} - {p^2}} \right)\)
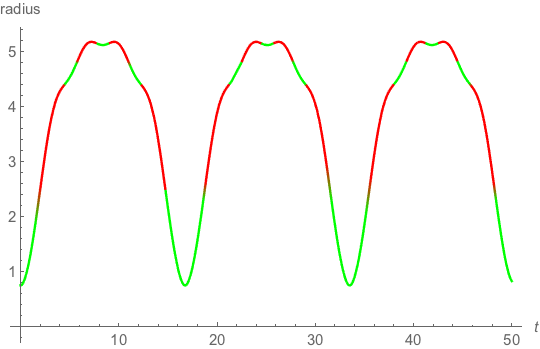
The pressure must go negative to get a bounce, but must be less than the energy density of matter at the same location.
\( - 1 \leqslant \frac{p}{\mu } \leqslant - \frac{1}{3}\)
The green area is where the pressure is in this negative region.
 Q&A (4871)
Q&A (4871) Reviews (203)
Reviews (203) Meta (439)
Meta (439) Q&A (4871)
Q&A (4871) Reviews (203)
Reviews (203) Meta (439)
Meta (439)